Introduction
Understanding Contextual Audiences
Programmatic advertising utilizes contextual audiences to target ads by considering the unique context of web pages or applications, rather than relying on personal data or user browsing histories. This approach has become crucial for advertisers due to the implementation of stricter privacy regulations. By emphasizing the content, themes, and intent associated with the environments in which ads are displayed, advertisers strategically adapt their focus. Personas often serve as the initial foundation for crafting efficient contextual targeting strategies.
- Example: When a user reads an article about fitness, it makes sense to show ads for gym memberships or health supplements. This alignment enhances the relevance of the advertisement without requiring the tracking of personal data.
Targeting contextual audiences enables advertisers to engage consumers authentically and effectively, aligning with their personas.
The Shift in Advertising Paradigms
In 2025, the growing emphasis on privacy and shifting consumer behavior necessitates a re-evaluation of traditional targeting methodologies, bringing accurate personas to the forefront.
Why Contextual Audiences Matter
- Evolving Privacy Regulations: Global privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, establish stringent guidelines on the collection, storage, and use of personal data. This transformation calls into question conventional data-driven audience targeting initiatives.
- Consumer Behavior: Increasing consumer awareness regarding digital footprints leads to heightened skepticism about targeted advertising based on personal data. Consumers are demanding transparency, a demand that contextual advertising meets by enhancing ad relevance while safeguarding privacy.
- Enhanced Relevance: Contextual targeting adeptly navigates privacy concerns while significantly improving ad relevance. By displaying advertisements that align with the content being consumed, advertisers can engage users effectively at key moments, thereby boosting click-through rates (CTR) and conversion rates.
Key Insights from Industry Sources
- ProgMedia Insights in “The Future of Advertising” asserts that the transition to contextual advertising represents a substantial transformation in ad conception, emphasizing delivering value over mere exposure.
- AdMetrics in “Understanding Contextual Advertising” states that advertisers who rapidly adapt to include contextual audiences in their strategies are likely to gain a competitive advantage. The report illustrates that aligning ad content with the surrounding page context leads to consistently higher engagement rates and improved return on investment (ROI) in campaigns.
The Implication for 2025
The advertising landscape in 2025 will be shaped by a deep integration of contextual audience targeting methodologies. This approach is set to enhance personalization by prioritizing context over identity, facilitating brands in creating more profound connections with consumers through relevant messaging. We believe that personas will play a crucial role in this shift toward contextual targeting.
With advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning, the ability of machines to comprehend content and sentiments is substantially improving. Understanding the nuances of consumer context is crucial for defining accurate personas. The industry’s movement towards contextual audiences highlights its flexibility and responsiveness to the evolving needs, expectations, and behaviors of consumers, each represented by distinct personas.
Contextual audiences are set to become a crucial element in driving performance within programmatic advertising. In an evolving privacy-focused environment, their role in engagement, user experience, and conversion cannot be underestimated. This shift towards relevance while upholding ethical advertising standards carries significant implications for how different personas interact with advertising content.
A Call to Action for Programmatic Experts
Programmatic advertising professionals must promptly reevaluate their current strategies due to the increasing prevalence of contextual audiences. By adopting these approaches, not only can they comply with stricter privacy regulations, but they can also align their advertising spending with the changing consumer environment and the evolving personas. In the upcoming sections, we will look at specific techniques and tools, such as personas, that enable effective utilization of contextual audiences, leading to the desired programmatic performance results.
What are Contextual Audiences?
Contextual audiences are groups of users identified based on the context of the content they are engaging with, rather than their past behavior, demographics, or specific interests. This method leverages the content of the page—including keywords, topics, and overall themes—to serve relevant advertisements. Advertisers can increase engagement and receptiveness without relying on personal data by aligning ads with the context in which they are placed, tailored to the relevant personas of their target audience.
Key Characteristics of Contextual Audiences
- Content-Centric: Focuses on page context rather than user history, enabling a less intrusive advertising experience tailored to specific personas.
- Data Privacy Compliant: With increasing regulations surrounding data privacy, such as GDPR and CCPA, contextual targeting adheres to compliance since it does not rely on cookies or personal tracking.
- Dynamic: Adjusts automatically to the content being consumed, providing real-time targeting capabilities that are essential in a fast-paced digital landscape. This flexibility ensures that advertisements remain relevant to the evolving personas of users.
Comparison to Traditional Targeting Methods
1. Behavioral Targeting
Behavioral targeting heavily relies on a user’s past online activities, tracking their browsing behavior and interactions across various websites. This technique utilizes cookies to collect data about users and raises significant privacy concerns, especially given evolving regulations that impact the creation and accuracy of personas.
- Advantages:
- Enables advertisers to target users who have shown interest in similar products or services.
- More personalized ad experiences can potentially increase conversion rates.
- Disadvantages:
- Vulnerable to privacy issues and user opt-out trends, which can restrict data accessibility.
- Can lead to ad fatigue as users may see the same ads repeatedly, causing decreased interest.
2. Demographic Targeting
Demographic targeting involves segmenting audiences based on characteristics such as age, gender, income level, and education.
- Advantages:
- Provides a straightforward method for targeting specific segments.
- Useful for products that inherently target predefined demographics.
- Disadvantages:
- Assumes that demographics alone dictate consumer behavior, overlooking the nuances of contextual relevance.
- Risks becoming outdated as consumer preferences and circumstances evolve.
3. Contextual Targeting
Contextual targeting, which encompasses contextual audiences, involves displaying ads based on the content being viewed rather than on personal data. This approach ensures that the advertisements are contextually relevant and timely, aligning with the defined personas of the target audience.
- Advantages:
- Reduces privacy concerns by avoiding the use of personal data, appealing to privacy-conscious personas.
- Engages users precisely at the moment they are consuming relevant content, thereby increasing click-through rates among targeted personas.
- Disadvantages:
- May lack the precision of behavioral targeting since it does not consider user interests beyond the immediate context, potentially missing out on nuanced personas.
- Requires a strong understanding of content categorization and relevance to optimize ad placements for various personas.
Evolution of Contextual Audiences
Historical Context
The evolution of digital advertising has witnessed several distinct phases. Initially, the landscape was dominated by tracking cookies, which allowed advertisers to build extensive profiles based on user behavior. However, growing privacy concerns and the discontinuation of cookies have significantly altered this paradigm, prompting a shift towards understanding and targeting specific personas.
From Cookies to Context
Recent shifts away from cookie-based targeting have propelled a resurgence in contextual targeting. Advertisers have begun to acknowledge that message relevance can drive engagement as effectively—if not more so—than traditional methods. According to MarketWatch, the rise of contextual targeting can be attributed to:
- The Implementation of Privacy Regulations: Stricter privacy laws restrict data collection, making it essential for advertisers to focus on the personas they aim to reach without relying on intrusive tracking methods.
- Rising Consumer Awareness: Increasing consumer awareness regarding privacy and data usage has influenced a preference for non-intrusive ad experiences that respect user personas.
The Future of Contextual Audiences
As we advance into 2025, the focus will increasingly shift toward contextual targeting, driven by:
- Advanced AI and Machine Learning: Capable of analyzing content at scale to identify appropriate audience alignments, this technique relies on accurate personas to find relevant contextual audience segments.
- Enhanced Algorithms: Determining context with greater precision, enabling highly relevant ad placements tailored to specific personas.
- Integration Across Multiple Channels: Including social media, video platforms, and offline media through programmatic capabilities, ensuring that various personas are effectively reached.
Understanding contextual audiences is vital for programmatic advertising experts looking to navigate the complexities of modern digital advertising. As advertisers transition their focus from user-specific data to contextually relevant content alignment, strategies to leverage personas become increasingly important in crafting effective and personalized advertising campaigns.
Why Contextual Audiences Matter in 2025
Strategic Advantages of Contextual Audiences
Persona-based contextual audiences play a critical role in the digital advertising landscape of 2025 by connecting advertisers and users, allowing for highly accurate targeting while upholding privacy and ensuring relevance.
Improved Targeting
- Granular Segmentation
- Persona-based contextual targeting allows advertisers to segment audiences based on the content they consume, ensuring that ads reach users with a natural affinity for relevant topics.
- Example: A campaign promoting eco-friendly products can effectively target content related to sustainability, green technology, or outdoor activities.
- Real-time Contextualization
- Utilizing advancements in machine learning and natural language processing, advertisers can react instantaneously to the context of a webpage, aligning ad placements with the current content.
- This method enables highly relevant advertising that resonates with user intent at that moment.
- Identification of Emerging Trends
- Analyzing contextual data can assist advertisers in swiftly identifying emerging user interests and trending topics. This leads to timely ad placements that capitalize on current conversations, improving engagement and conversion rates.
Enhanced Creative Relevance
- Dynamic Creative Optimization (DCO)
- Contextual audiences facilitate dynamic creative management systems that serve personalized ad creatives aligned with the user’s current content.
- Example: A user reading a travel blog may see ads featuring flights or vacation packages tailored to their interests, enhancing the overall ad experience.
- Increased Engagement
- Contextually relevant ads are more likely to capture a user’s attention and prompt interaction. Research published in the Digital Privacy Journal indicates that contextually-targeted ads generate higher engagement rates compared to traditional targeting methods.
- Such engagement can lead to a greater likelihood of conversion, reinforcing the value of connecting ads with the appropriate context.
- Creative Tailoring Opportunities
- Advertisers can adapt their messaging based on the surrounding content. For example, users engaged with sports journalism are more likely to respond positively to ads featuring sports apparel or events, potentially leading to heightened brand affinity.
Privacy Compliance
- Adapting to Regulatory Changes
- With increasing scrutiny on data privacy, contextual targeting emerges as a compliant alternative. Unlike behavioral targeting, which depends on user data and tracking, contextual targeting focuses on the content itself, significantly reducing privacy concerns.
- By prioritizing context over personal data, advertisers can mitigate risks associated with ongoing regulatory changes and heightened user awareness of data privacy.
- Trust Building with Consumers
- Many users are becoming increasingly wary of invasive targeting methods; hence, contextually relevant ads can help foster trust. When consumers feel that brands respect their privacy and provide non-intrusive ads, they are more likely to engage positively.
- Thus, contextual advertising adheres to compliance standards while reinforcing a brand’s commitment to consumer respect and ethical advertising practices.
- Emerging Privacy-centric Technologies
- With new technologies focusing on privacy-conscious advertising, contextual audiences will lead the way. Industry initiatives emphasizing first-party data and non-personalized targeting options are being developed, reinforcing contextual strategies that uphold user privacy.
Conclusion
In a landscape where relevance, engagement, and compliance are paramount, contextual audiences stand out as a pivotal strategy for programmatic advertisers in 2025. By leveraging the advantages outlined above, advertisers can navigate a path that not only drives performance but also aligns with industry standards and consumer expectations. Adopting this approach is not merely a trend; it is imperative for sustainable success in the future of digital advertising.
Key Trends Influencing the Use of Contextual Audiences
Understanding key trends influencing the use of contextual audiences is paramount in the rapidly evolving landscape of programmatic advertising. These trends shape how advertisers engage with consumers and dictate the strategic frameworks programmatic experts must adopt to optimize their campaigns. Below are critical trends set to influence contextual audience strategies in 2025.
1. Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is revolutionizing how advertisers leverage contextual data. Key advancements include:
- Enhanced Data Processing: AI technologies can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, allowing advertisers to identify contextually relevant opportunities quickly. Machine learning algorithms can learn from past performance and predict which contexts resonate best with target audiences.
- Contextual Prediction Models: Developments in natural language processing (NLP) enable better understanding and interpretation of content on webpages. Predictive models can assess the sentiment and mood conveyed in online articles, tailoring ads to ensure they align with that context.
- Automated Content Creation: AI-driven tools help create personalized ad copies that fit specific contexts, improving the relevance of ads shown to users. AI platforms generating tailored messages for varying contexts have significantly enhanced engagement rates.
Example: Suppose a user is reading an article about sustainable practices. An AI algorithm could recognize this context and serve eco-friendly product ads, aligning brand messaging with the user’s current interests and sentiments.
2. Shifts in Consumer Sentiment
Consumer behaviors and attitudes towards digital ads continue to evolve. Key factors include:
- Increased Privacy Awareness: Consumers are more aware of privacy issues and are demanding greater transparency in how their data is used. According to Ad Age, a significant portion of users prefer contextual advertisements—those that don’t depend on personal data but are relevant to the content they consume—over personalized ads that track their behavior.
- Demand for Relevant Content: Audiences prefer ads that resonate with their present contexts, showing an inclination towards meaningful interactions. This leads to a rising demand for contextual advertising, fostering a more organic connection with users.
- Skepticism Towards Targeting Techniques: As skepticism grows around targeting techniques frequently associated with invasive practices, advertisers must pivot towards strategies that respect user intent while leveraging contextual signals.
Example: If a consumer is reading about family health tips, they may appreciate seeing ads for organic food options or health products, creating an authentic link without the discomfort of personal data usage.
Reference: Ad Age highlights the evolving consumer preferences towards contextual ads over personalized targeting based on data privacy concerns.
3. The Decline of Third-Party Cookies
The phasing out of third-party cookies significantly impacts advertising strategies, particularly in audience targeting:
- Rise of First-Party Data: With third-party cookies becoming obsolete, contextual advertising is primed to fill the gap. Advertisers increasingly rely on first-party data—information gathered directly from users—coupled with contextual insights to effectively reach audiences while maintaining privacy standards.
- Shift to Contextual Signals: Programmatic experts will focus on contextual signals—such as keyword associations, webpage content, and real-time data analysis—to create relevant campaigns. This shift indicates a potentially higher demand for contextual audience strategy over traditional audience targeting.
- Legislative Changes and Compliance: With data privacy regulations tightening (GDPR, CCPA), utilizing contextual insights complies more readily with legal standards. Marketers must stay informed on legislation to ensure their strategies adhere to best practices.
Example: In a world where tracking cookies are becoming obsolete, an automotive brand may analyze trending topics in the transportation sector and align their advertising efforts with current content addressing electric vehicles, furthering engagement through relevancy without the need for tracked user behavior.
Conclusion
The interplay of AI advancements, shifts in consumer sentiment, and the decline of third-party cookies shapes the landscape in which contextual audience strategies operate. Staying attuned to these trends will empower programmatic experts to refine their approaches, ensuring that their campaigns resonate meaningfully and effectively amidst the evolving digital advertising ecosystem.
By anticipating these shifts and adapting their strategies accordingly, advertisers can harness the power of contextual audiences to drive programmatic performance in 2025 and beyond.
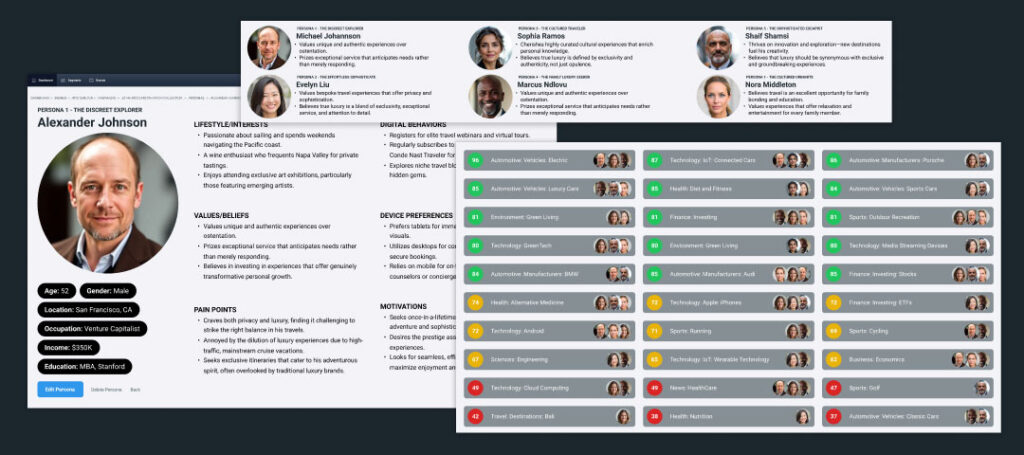
Building Effective Contextual Audience Profiles
Understanding Contextual Audience Profiles
Contextual audience profiles are essential constructs in programmatic advertising, enabling advertisers to identify and engage users based on content-related clues rather than personal data. With tightening privacy regulations and the phasing out of cookies, contextual targeting has emerged as a robust method for meaningfully reaching consumers.
Importance of Contextual Audience Profiles
A systematic approach to building contextual audience profiles not only allows advertisers to craft targeted campaigns but also maximizes return on investment (ROI). By understanding user intent through contextual signals, brands can deliver relevant messages to consumers who are actively engaged with topics related to their products or services.
Steps to Create Contextual Audience Profiles
1. Data Collection
Data collection is a critical first step in constructing effective contextual audience profiles. Utilize a combination of qualitative and quantitative data:
- Content Analysis:
- Scrutinize the content of websites or platforms relevant to your industry.
- Identify key themes, topics, and keywords that resonate with your target audience.
- Behavioral Insights:
- Leverage behavioral data from platforms like Google Analytics or social media insights to understand which content engages your audience. Consider metrics such as:
- Average time on page
- Bounce rates
- Click-through rates (CTR)
- Leverage behavioral data from platforms like Google Analytics or social media insights to understand which content engages your audience. Consider metrics such as:
- Surveys and Feedback:
- Conduct surveys or focus groups to capture audience sentiment directly.
- Questions regarding preferences, interests, and online behavior can help refine your contextual audience profiles further.
2. Identifying Contextual Signals
Once relevant data is collected, identifying contextual signals becomes crucial. These signals refer to thematic or categorical attributes derived from the user’s environment or behavior:
- Keywords:
- Extract keywords from your content analysis that align with user intents.
- Tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs can assist in discerning relevant search terms.
- Content Categories:
- Classify your audience’s engagement into various categories (e.g., News, Lifestyle, Technology).
- This classification provides insight into where your target audience spends their time online.
- Emotional Tone and Sentiment:
- Analyze the emotional tone of content using tools such as IBM Watson Natural Language Understanding, which can gauge sentiment and enrich your understanding of audience interactions.
3. Segmentation of Audience
Following the identification of contextual signals, the next step is to segment your audience based on specific characteristics:
- Interests:
- Differentiate between audience interests drawn from contextual signals, such as technology enthusiasts versus travel aficionados.
- Purchase Intent:
- Assess the likelihood of purchase based on engaged content.
- For example, a user reading product comparisons on tech blogs may signal higher intent than casual browsing on travel sites.
- Demographic Insights:
- While contextual profiling primarily relies on content engagement, understanding the demographic background (age, gender, location) can further refine campaigns for targeted segments.
4. Build and Implement Profiles
Once segmentation is complete, create detailed audience profiles to inform your advertising strategy:
- Profile Attributes:
- Each profile should outline attributes like demographics, interests, behavioral patterns, and contextual engagement comprehensively.
- Creative Messaging:
- Tailor messaging that resonates specifically with each contextual audience.
- Example: When targeting a tech-savvy young adult, employ innovative language that reflects the latest trends.
- Programmatic Setup:
- Use demand-side platforms (DSPs) to implement your contextual profiles.
- Ensure your selected DSP effectively parses contextual signals to deliver your ads to the most relevant placements.
5. Monitor and Adjust
Building effective contextual audience profiles is not a one-time endeavor. Continuous monitoring and adjustments are essential for maintaining relevance in a rapidly evolving digital landscape:
- Performance Metrics:
- Regularly track metrics like CTR, conversion rates, and engagement rates to evaluate the effectiveness of your contextual strategies.
- Iterative Improvements:
- Use insights from campaign performance to refine audience profiles and contextual signals regularly.
- If a specific content category underperforms, adjust your approach accordingly.
- Feedback Loop:
- Establish a mechanism for gathering audience reactions to your ads, indicating whether your messaging and contextual targeting resonate meaningfully.
Conclusion
By following these detailed steps, programmatic advertising experts can effectively build rich contextual audience profiles that enhance campaign precision and performance. Data analysis and behavioral insights provide the foundational intelligence necessary for creating campaigns that resonate deeply with consumers, ultimately driving greater engagement and ROI.
Implementing Contextual Targeting in Campaigns
Contextual targeting has emerged as a powerful strategy for achieving higher relevance and engagement in programmatic advertising. By aligning your campaigns with the defined personas of your target audience, you can ensure that your ads resonate more effectively. This section delves into actionable steps for integrating contextual targeting into your campaigns, the tools and platforms to leverage, and best practices to optimize your results while considering the unique personas of your audience.
Understanding Contextual Targeting
Contextual targeting uses the content of the webpage where the ad appears to determine relevance. By matching ads to content categories that align with the interests and personas of your audience, brands can effectively reach their target segments based on their current interests, leading to increased engagement and improved conversion rates.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
- Define Your Objectives:
- Identify your campaign goals. Are you looking to increase brand awareness, drive traffic, or boost sales? Understanding the personas you aim to target will help shape the way you implement contextual targeting to meet these objectives effectively.
- Select Relevant Content Categories:
- Use tools that can categorize content accurately to match your target personas. For instance, if your brand offers eco-friendly products aimed at environmentally conscious personas, you might want your ads to appear on sustainability-related sites. Consider categories like:
- News
- Fitness
- Technology
- Travel
- Use tools that can categorize content accurately to match your target personas. For instance, if your brand offers eco-friendly products aimed at environmentally conscious personas, you might want your ads to appear on sustainability-related sites. Consider categories like:
- Utilize Contextual Targeting Platforms:
- Leverage tools and platforms designed to enhance your contextual targeting capabilities, tailored to your specific personas. Notable examples include:
- Demand-Side Platforms (DSPs): Platforms like The Trade Desk and MediaMath offer advanced contextual targeting features that allow advertisers to set granular targeting options.
- Contextual Advertising Networks: Networks such as AdRoll specialize in placing ads on sites that align with the chosen content categories.
- Leverage tools and platforms designed to enhance your contextual targeting capabilities, tailored to your specific personas. Notable examples include:
- Incorporate Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Determine how you will measure the success of your contextual campaigns. Key KPIs may include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Conversion Rate
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
- Determine how you will measure the success of your contextual campaigns. Key KPIs may include:
- Test and Optimize Your Strategy:
- Begin with A/B testing different contexts and ad placements to see which personas respond best. Monitor performance closely and adjust targeting parameters based on real-time data.
- Example: If ads for athletic shoes perform best on fitness article pages, consider increasing your bid for those contexts.
- Leverage Machine Learning and AI:
- Advanced platforms utilize machine learning to optimize placements in real-time. Engage with tools that can analyze content trends, helping to identify promising contextual opportunities.
- Use Audience Insights:
- Analyze past campaign data to understand which contexts produced the highest engagement among your personas. Consider audience segmentation based on demographics, interests, and past interactions to tailor content categories more effectively.
Tools and Platforms for Contextual Targeting
- Google Ads: Offers Display Advertising that allows advertisers to select contextual targeting options relevant to their product or service.
- AdRoll: Provides tools that combine retargeting and contextual targeting features, helping to reach users across the web.
- Taboola and Outbrain: Effective platforms for native advertising that can be tailored to appear in surrounding content relevant to your ad.
Best Practices for Successful Campaigns
- Stay Relevant: Ensure that your ads are directly related to the content on the page. This synergy not only enhances user experience but also fosters trust in your brand.
- Diversify Contextual Placements: Don’t rely solely on one type of context. Experiment with diverse platforms and content types to broaden your reach.
- Monitor Industry Trends: Contextual advertising is evolving. Stay updated on new technologies and methodologies introduced in the industry.
- Focus on Brand Safety: Regularly review your contextual targeting strategies to ensure your ads are being placed on reputable sites, avoiding associations with harmful or misleading content.
By integrating these steps and leveraging the right tools and platforms, programmatic experts can harness the power of contextual audiences to enhance their ad campaigns in 2025 and beyond. Contextual targeting is not only a more relevant approach to reaching potential customers but, when executed correctly, it leads to deeper customer engagement and improved brand performance.
Measuring Success and Performance Metrics
When implementing contextual audiences in programmatic advertising, understanding how to measure success is critical. This section delves into the key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that experts need to assess the effectiveness of their media campaigns closely. Accurate measurement not only provides insights for refining strategies but also establishes the return on investment (ROI) essential for justifying ad spend and making informed decisions.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Viewability Rate
- Definition: The percentage of ads that are actually seen by users, as opposed to being served without visibility.
- Importance: A high viewability rate ensures that ads reach an actual audience, increasing the chances of engagement.
- Example: If 50 out of 100 served ads are viewed, your viewability rate would be 50%.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Definition: A ratio of users who click on the ad to the total number of users who view the ad.
- Importance: CTR serves as a direct indicator of the ad’s effectiveness in prompting user action.
- Example: If your ad receives 20 clicks out of 1,000 views, your CTR is 2%.
- Conversion Rate
- Definition: The percentage of users who complete a desired action after clicking on an ad (e.g., making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter).
- Importance: The conversion rate connects ad performance with business results, demonstrating the effectiveness of ad spend.
- Example: If 100 users click through and 5 make a purchase, your conversion rate is 5%.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)
- Definition: The cost associated with acquiring a customer through advertising, calculated by dividing total ad spend by the number of conversions.
- Importance: Understanding CPA is crucial for evaluating the efficiency of expenditure relative to outcomes.
- Example: If you spent $500 on an ad campaign that resulted in 20 purchases, your CPA would be $25.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
- Definition: A metric measuring the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising.
- Importance: Assessing ROAS helps marketers determine the financial effectiveness of campaigns, guiding future budget allocations.
- Example: If you spent $1,000 on an ad and generated $5,000 in revenue, your ROAS would be 5.
- Engagement Metrics
- Definition: Metrics encompassing likes, shares, comments, and overall user interaction with the ad on various platforms.
- Importance: High engagement metrics not only indicate ad relevance but also highlight the potential to foster community and brand loyalty.
- Example: An ad with 100 likes and 20 shares from 1,000 views demonstrates strong engagement.
Additional Metrics
- Brand Lift
- Definition: A measure of the increase in brand awareness or favorability that results from an advertising campaign.
- Importance: It indicates how effectively contextual advertising resonates with target audiences on an emotional level.
- Measurement: Typically assessed through surveys before and after the campaign.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- Definition: An estimate of the total revenue that a customer will generate throughout their ongoing relationship with your brand.
- Importance: A higher CLV suggests that a campaign attracts long-term customers, justifying greater upfront advertising expenses.
- Example: If a customer is estimated to generate $1,200 over their lifetime, investing $100 in acquisition becomes a strategic advantage.
- Attribution Models
- Definition: Frameworks assigned to determine how credit for conversions is distributed among various touchpoints along the customer journey.
- Importance: Understanding which components of your campaigns drive conversions is vital for optimization. This includes first-click, last-click, or multi-touch attribution methods.
- Example: If a user sees an ad and later makes a purchase through a search, the attribution model can aid in determining how to assign value to that ad.
The Importance of Measurement
In programmatic advertising, measurement is a crucial activity. Here’s why effective measurement is paramount:
- Iterative Improvement: Continuous assessment aids in fine-tuning campaigns. Clear metrics enable advertisers to swiftly adjust strategies based on performance data, boosting overall effectiveness.
- ROI Justification: Marketers need to substantiate the value of their expenditures. Quantitative data regarding campaign performance aids in demonstrating ROI, facilitating budget approvals for future initiatives.
- Competitive Analysis: Monitoring KPIs allows advertisers to benchmark against industry standards, revealing areas for improvement compared to competitors.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Armed with precise metrics, marketers can make informed decisions regarding future campaign directions and strategies, leading to better resource allocation and improved outcomes.
In conclusion, for programmatic advertising experts, familiarizing themselves with various KPIs and metrics is vital to leveraging contextual audiences for enhanced performance. Each measurement plays a crucial role in crafting a landscape of data that informs actionable decisions, ensuring immediate results while fostering long-term advertising success.
Conclusion
As we conclude our in-depth exploration of utilizing contextual audiences to drive programmatic performance in 2025, it is imperative to summarize our key insights and emphasize the importance of adopting this approach in the rapidly evolving digital advertising environment.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Contextual Targeting’s Relevance:
- Contextual targeting uses the relevance of surrounding content to deliver ads in real-time. With new consumer privacy norms tightening, contextual relevance stands out as a powerful mechanism that respects user privacy while offering valuable advertising opportunities.
- Enhanced Engagement and Performance:
- Advertising to contextual audiences allows marketers to tailor ads to users’ interests based on the content they are currently engaged with. This strategic alignment often results in higher engagement rates and improved performance metrics, such as CTR and conversion rates.
- Adapting to Changes in Data Privacy:
- With the increasing emphasis on regulations concerning personal data usage, transitioning to contextual audience targeting offers a compliant alternative. This adjustment enables brands to sustain targeting effectiveness without relying on personal identifiers, which face growing restrictions.
- Leveraging Advanced Technologies:
- The application of machine learning and AI-driven tools enhances the ability to create precise contextual audiences. These advanced technologies analyze extensive datasets, ensuring that ads are displayed in the most relevant contexts, ultimately maximizing consumer interaction potential.
- Seamless Integration into Existing Strategies:
- Employing contextual audiences does not necessitate a complete revamp of existing programmatic strategies. By incorporating contextual targeting alongside conventional methods, marketers can develop more resilient and adaptive campaigns.
- Continuous Optimization and Learning:
- An iterative approach that includes feedback loops and performance monitoring is critical for refining contextual targeting strategies. This ongoing optimization enables marketers to discern effective practices and remain responsive to shifting consumer behaviors.
Next Steps for Exploration
To deepen your understanding and enhance your implementation of contextual audiences, consider the following actions:
- Experiment with Contextual Tools: Engage with available tools and platforms designed for contextual advertising. Test various formats and placements to identify those yielding the highest engagement rates for your campaigns.
- Stay Updated on Industry Trends: Keep abreast of thought leaders and publications focusing on programmatic advertising and contextual strategies analysis. The resources referenced in this guide, such as “Future Insights for Programmatic Advertising” by HubSpot (HubSpot) and “A Look Ahead: The Future of Contextual Advertising” by WARC (WARC), can provide invaluable insights and data.
- Cultivate Cross-Department Collaboration: Foster collaboration with content creators, SEO specialists, and analytics teams to ensure that themes and messages resonate with contextual audience targeting. This teamwork can lead to enriched creative outputs and more targeted advertising strategies.
- Participate in Industry Workshops and Webinars: Attend conferences, webinars, and workshops centered on programmatic advertising practices. Engaging with industry experts will not only enhance your knowledge but also facilitate the exchange of insights with peers facing similar challenges.
Final Thoughts
Adopting contextual audiences signifies a forward-thinking approach within programmatic advertising. It harmonizes with the industry’s transition towards prioritizing privacy while effectively engaging consumers. By maintaining awareness, embracing experimentation, and embedding these strategies within your broader advertising frameworks, you can elevate your campaigns to achieve greater relevance, enhanced performance, and sustained success in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Ready to transform your advertising strategy with advanced contextual targeting? Book a demo today to see our innovative platform in action. We build AI-driven personas from your campaign brief, map them to contextual audience segments, and deliver a Deal ID for seamless activation. Our fully managed service makes it easy to test, optimize, and uncover untapped audiences while improving campaign performance. Discover how leveraging personas can enhance your campaign relevance and drive superior results in a privacy-focused advertising landscape.
References
- ProgMedia Insights. The Future of Advertising.
- AdMetrics. Understanding Contextual Advertising.
- Digital Privacy Journal. Privacy and Programmatic Advertising.
- ClickZ. The Need for Relevance in Digital Advertising.
- Research and Markets. “KPIs that Matter in Programmatic Advertising”.
- MarTech Today. “Evaluating Campaign Performance”.
- The Drum. “Successful Campaigns in Programmatic Advertising”.
- Campaign US. “Learning from the Leaders: Contextual Audience Success Stories”.
- TechCrunch.
- Ad Age.
- HubSpot. Future Insights for Programmatic Advertising.
- WARC. A Look Ahead: The Future of Contextual Advertising.
- Digiday. The Best Tools for Programmatic Advertising.
- AdExchanger. Harnessing Technology for Contextual Targeting.